How does artificial intelligence work? A Simple Guide

At its most fundamental level, artificial intelligence is all about using sophisticated algorithms to sift through massive amounts of data. The goal is to spot patterns, learn from them, and then use that understanding to make predictions or carry out a specific task.
It's not some kind of digital magic. Think of it more like a very, very dedicated student learning a new subject through endless study and practice. This process is what allows AI to graduate from just following basic programmed instructions to making genuinely intelligent decisions on its own.
How AI Actually Learns and Makes Decisions
So, how does this "learning" actually happen? Let's pull back the curtain.
Picture an AI model as a brand-new student, but one without any intuition or common sense. It starts as a blank slate and can only learn from the information it's given. This "student" is fed enormous datasets—we're talking millions of images, entire libraries of text, or decades of financial records—and its job is to find the hidden connections buried within all that information.
This learning process is driven by algorithms, which are really just sets of rules and statistical methods. The AI isn't simply memorizing the data. It's building a flexible mental model of the subject. For example, after analyzing thousands of cat photos, it starts to understand the key features—whiskers, pointy ears, certain fur textures—that scream "cat." This is what allows it to correctly identify a cat in a photo it’s never encountered before.
To really get a handle on what AI is (and isn't), it helps to know the main categories people talk about. These aren't just technical terms; they represent different levels of intelligence and capability, from the AI we use every day to the stuff of science fiction.
The Three Main Categories of Artificial Intelligence
This table gives you a quick overview of the different types of AI you'll hear about, which provides some helpful context for the technologies we'll dive into.
| AI Category | Description | Current Status |
|---|---|---|
| Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI) | An AI that is an expert in one specific area or task. | This is the only type of AI that actually exists today and is in widespread use. |
| Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) | A hypothetical AI with human-like intelligence that can learn, understand, and apply its knowledge to solve any problem. | AGI is purely theoretical right now. We haven't built anything close to it. |
| Artificial Superintelligence (ASI) | An AI that would surpass human intelligence in virtually every field, including scientific creativity and general wisdom. | This remains a concept explored mostly in futuristic discussions and fiction. |
Getting this distinction is crucial. Every single AI tool you interact with, from Siri or Alexa to the recommendation engine on Netflix, is a form of Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI).
These systems are absolute masters of their specific domains, but they have no ability to step outside them. With that foundational knowledge in place, we can start to explore the specific engines—like machine learning—that truly power modern AI.
Understanding The Three Layers of Modern AI
To really get a handle on how artificial intelligence works, it's helpful to picture it like a set of Russian nesting dolls. Each doll you open reveals a more specific, powerful technology inside. The biggest, outermost doll is Artificial Intelligence (AI)—the whole big-picture idea of making machines that can think or act in intelligent ways.
But when you open that AI doll, you find the real engine driving almost all the progress we see today: Machine Learning (ML). This is where the "learning" actually happens. Instead of being painstakingly programmed with a mountain of rigid "if-then" rules, ML systems are trained on massive amounts of data, learning to spot patterns and make decisions all on their own.
So, if AI is the car, Machine Learning is the incredible, self-improving engine that makes it run.
The Machine Learning Engine
At its core, machine learning is all about pattern recognition. These systems sift through huge datasets—everything from neatly organized spreadsheets (structured data) to messy stuff like images and audio files (unstructured data)—and get better at their jobs over time without a human programmer tweaking their code for every new scenario. This data is the fuel for the system, and managing it well is critical. If you're curious about data management, our guide on how to use cloud storage offers some great insights.
A cornerstone of machine learning is the neural network, a concept loosely modeled on the web of neurons in the human brain. These networks are built from layers of interconnected nodes, or "neurons," that process information. As the network trains, it constantly adjusts the connections between these nodes to get better at predicting the right answer and minimize its errors. This data-first approach is why the AI market is growing so rapidly, a trend detailed by researchers at MarketsandMarkets.com.
The diagram below shows where the AI we have today fits into the bigger picture, and where it might be headed.
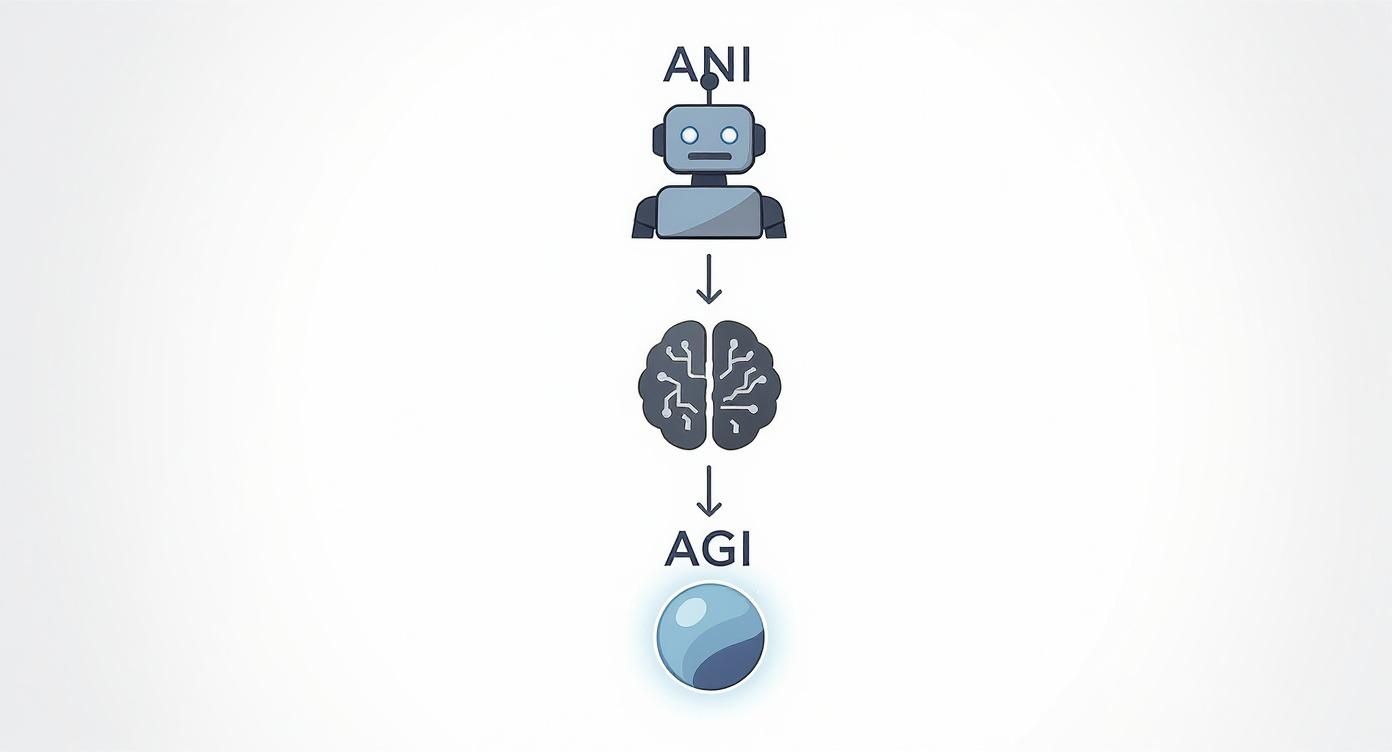
As you can see, everything we currently call "AI" is actually Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI). It’s technology designed to do one specific task really well, but it's the foundation for everything that might come next.
The Deepest Layer: Deep Learning
Now, let's open up the Machine Learning doll. Tucked inside is Deep Learning (DL), an even more specialized and potent subset of ML. Deep learning takes the neural network concept and kicks it up a notch, using complex networks with many, many layers—which is where the "deep" part of the name comes from.
Think of it this way: if machine learning is a talented chef who learns recipes by tasting different combinations of ingredients, deep learning is the master sommelier who can pick out impossibly subtle notes in a glass of wine—the soil, the weather from that year, the type of barrel it was aged in. That incredible depth allows it to solve far more complex problems.
Key Takeaway: AI is the big idea. Machine Learning is the process of teaching a computer to learn from data. And Deep Learning is an advanced ML technique using massive, multi-layered neural networks to crack incredibly complex challenges.
This layered structure is exactly what makes today's most impressive AI tools possible. For instance:
- Netflix Recommendations: That movie queue that seems to read your mind? That’s powered by machine learning. It analyzes your viewing history and compares it to millions of others to guess what you’ll want to watch next.
- Facial Recognition: Unlocking your phone with your face relies on deep learning. It requires a much more sophisticated level of pattern recognition to analyze the unique contours, shadows, and dimensions of a human face.
The Three Ways an AI Model Is Trained
An AI model doesn't just appear out of thin air knowing how to solve problems. It starts as a blank slate and has to be taught, kind of like a new student on their first day of class. The way it learns comes down to one of three core training methods, each designed to turn raw data into a specific kind of intelligence.
These methods are the secret sauce behind almost every AI you interact with, from the spam filter in your email to the AI opponents in a video game. Each approach is built for a different kind of problem.

Supervised Learning: The Flashcard Method
The most common approach by far is Supervised Learning. Imagine studying for a test with a massive stack of flashcards. On one side is a question, and on the back is the correct answer. This is exactly how supervised learning works. The AI is given a huge dataset where every single piece of data is neatly labeled with the right outcome.
Let's say you're training an AI to spot cats in photos. You'd feed it millions of images, each one meticulously tagged as either "cat" or "not a cat." The model makes a guess for each image, checks its answer against the label, and then fine-tunes its internal logic to get better. It does this over and over, slowly learning the visual patterns—pointy ears, whiskers, fur—that define a cat.
This method is perfect for tasks with clear right-or-wrong answers, like:
- Spam Filters: Learning to tell junk mail from important messages based on thousands of past examples.
- Medical Scans: Analyzing X-rays to identify potential signs of disease that have been confirmed by doctors.
- Housing Prices: Predicting a home's value based on features like its size, location, and the sale prices of similar homes.
Unsupervised Learning: Finding Patterns on Its Own
But what happens when you don't have a perfectly labeled dataset? That's where Unsupervised Learning steps in. With this method, you give the AI a giant, messy pile of data and just ask it to find interesting patterns on its own. It’s like being handed a disorganized library and asked to sort the books into logical groups, without any prior knowledge of genres like "sci-fi" or "history."
The algorithm sifts through all the information, looking for natural clusters and hidden structures. This is a powerful way to discover insights that a human might never notice. For example, a music streaming service could use it to group listeners with similar tastes, creating "taste profiles" for better recommendations—all without knowing why those users like the same songs.
This approach is the bedrock of market segmentation, where companies find distinct customer groups in their data to make their marketing more relevant and effective.
Reinforcement Learning: Learning Through Trial and Error
The third method, Reinforcement Learning, is all about learning from experience. Think of it like training a puppy. You don't hand it a manual on good behavior. Instead, you reward it with a treat for sitting (a positive signal) and discourage it from chewing on the sofa (a negative signal).
An AI agent is placed in an environment—often a simulation—where it can take actions. It learns by getting rewards or penalties for the outcomes of those actions. Over millions of attempts, it develops a strategy to maximize its total reward. This trial-and-error process is perfect for complex, dynamic situations where the goal is to make a series of good decisions, not just find a single right answer.
Comparing AI Learning Methods
To make it clearer, here’s a quick breakdown of how these three fundamental training methods stack up against each other.
| Learning Method | How It Works | Common Example |
|---|---|---|
| Supervised | Learns from labeled data with correct answers provided. | An email client identifying spam based on examples of known junk mail. |
| Unsupervised | Finds hidden patterns and structures in unlabeled data on its own. | A streaming service grouping users with similar movie preferences. |
| Reinforcement | Learns by taking actions and receiving rewards or penalties. | A self-driving car learning the best route by getting positive feedback for safe, efficient moves. |
Each method serves a different purpose, but they all share one critical dependency: data.
AI algorithms are incredibly data-hungry. The amount of digital data created worldwide shot past 79 zettabytes in 2021 and is only accelerating, providing the raw fuel for these models. Some systems need millions of labeled examples to become proficient, and their success hinges on the quality and diversity of that information. You can dig deeper into the AI market's reliance on data with research from Cargoson.com.
Seeing AI at Work in Your Daily Life

Artificial intelligence isn't some futuristic idea from a movie. It's already here, quietly running in the background of your everyday life. The gadgets and apps you use every day are perfect examples of AI in action, working in practical and tangible ways.
When you ask your phone for the weather or get a song recommendation, you're interacting with an AI model. Seeing these examples helps connect the dots between the abstract training concepts we talked about and the real results you experience. You probably use specialized AI dozens of times a day without a second thought.
AI That Understands Your Voice
Every time you talk to a voice assistant like Siri, Alexa, or Google Assistant, you're tapping into Natural Language Processing (NLP). This is the field of AI that’s all about teaching computers to make sense of human language—not just the words, but the intent behind them.
Your smart speaker doesn't just "hear" you. An NLP model is working behind the scenes to break down your sentence, figure out what you're asking for, and pull together the right information to give you a useful answer. It’s a pretty sophisticated process that turns the sound of your voice into data it can act on.
AI That Sees the World
Then there's Computer Vision, which is all about giving machines the ability to interpret the visual world. This is the technology that lets a self-driving car identify a pedestrian, read a stop sign, or stay in its lane.
But it’s also working in much simpler, more common ways:
- Photo Tagging: When your smartphone or a social media app suggests tagging a friend in a photo, it's using computer vision to recognize their face.
- Product Search: Ever used an app where you can snap a picture of a product to find it online? That's computer vision analyzing the image to find similar items.
To get this good, these systems are trained on millions upon millions of images, learning to identify objects from different angles and in all sorts of lighting.
Key Insight: The AI in your daily life is highly specialized. The AI that understands speech (NLP) is a completely different tool from the one that recognizes faces (Computer Vision). Both, however, learn from massive datasets to master their specific jobs.
AI That Predicts Your Next Move
Ever wonder how Spotify serves up a "Daily Mix" that just gets you? Or how Amazon seems to know exactly what you want to buy next? That’s the magic of Recommendation Engines.
These AI systems are experts at unsupervised learning. They analyze your past behavior—songs you've liked, movies you've watched, or products you've bought—and cross-reference it with the habits of millions of other people. By identifying patterns and grouping users into "taste clusters," the AI gets remarkably good at predicting what you'll enjoy next.
All the data that powers these predictions is stored on huge networks of servers. If you're curious about the infrastructure behind it all, you can learn more about how cloud storage works in our detailed guide. These recommendation algorithms are always learning and fine-tuning their suggestions, making your experience feel more and more personal.
Exploring The Challenges and Future of AI
For all of its incredible capabilities, AI isn't perfect. To really get a handle on how it works, we have to look at the tough questions and real-world challenges that come with it.
At the heart of the matter is a simple truth: an AI is only as good as the data it learns from. This leads directly to one of the biggest problems in the field today: AI bias.
If you train a model on data that reflects historical human prejudices, the AI will learn those biases and, in many cases, make them even worse. Imagine an AI designed to screen job applicants. If it's trained on decades of hiring data where men were predominantly chosen for leadership roles, it might start to automatically penalize qualified female candidates. The AI isn't trying to be discriminatory; it's just repeating the patterns it was shown.
The Problem of Privacy and Data
Another massive hurdle is data privacy. Modern AI models are hungry for information, and they need enormous amounts of it to get smarter and more accurate. Everything from your search history to your GPS location can be used to fuel the personalized services we use every day.
This hunger for data raises some serious questions. How is our information actually being used? Who gets to see it? And how can we be sure it's safe from being stolen or misused? Finding the right balance between building helpful technology and protecting our personal privacy is one of the most difficult tightropes developers and regulators have to walk.
A Critical Perspective: The goal isn't just to build smarter AI, but to build responsible AI. Ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability is essential to earning public trust and making sure the technology benefits everyone, not just a select few.
Looking Ahead at AI's Potential
Even with these obstacles, the future of AI is undeniably bright. Researchers are pointing its problem-solving power at some of humanity's biggest challenges, from finding new medical cures to creating better models for climate change. AI's ability to sift through mind-bogglingly complex data at speeds no human ever could is unlocking breakthroughs we once only dreamed of.
The sheer economic scale of AI shows just how deeply it's becoming woven into our world. The global AI market was valued at around USD 371.7 billion in 2025 and is projected to soar to USD 2.4 trillion by 2032. This explosive growth, detailed in reports from firms like Precedence Research, is fueled by massive investments in the cloud computing and specialized hardware needed to run these powerful systems.
The path forward is all about navigating these ethical minefields while thoughtfully chasing the incredible opportunities. The real key is building AI that is not only powerful but also fair, transparent, and aligned with our best interests. Getting that right will decide whether we create a future where AI truly helps solve our biggest problems and improve life for everyone.
Frequently Asked Questions About How AI Works
Even with the basics covered, a few common questions always seem to pop up. Let's tackle some of the most frequent points of confusion head-on to help you get a clearer picture of how AI really works.
Think of this as tying up the loose ends.
What Is the Real Difference Between AI and Machine Learning?
This is easily the biggest source of confusion, but the distinction is pretty straightforward once you see it. It all comes down to the big idea versus the specific tool used to build it.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the whole field—the grand ambition of making machines that can do things that normally require human smarts. It's the destination we're trying to reach.
- Machine Learning (ML) is the main vehicle we're using to get there. It's the practical technique of feeding a computer tons of data and letting it figure out the patterns on its own, instead of programming it with step-by-step instructions.
Simply put, AI is the what, and machine learning is the how. Just about every AI tool you interact with today, from Netflix recommendations to spam filters, is powered by machine learning.
Can AI Actually Think for Itself or Have Emotions?
Nope. At least, not in any way we would recognize as human. The AI we have today is called Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), which is a fancy way of saying it's incredibly good at one specific thing. It can crush a human at chess or spot manufacturing defects on an assembly line, but it has zero self-awareness, common sense, or feelings.
When an AI writes a poem that sounds sad, it isn't feeling sad. It's just exceptionally good at recognizing and recreating the patterns of words that we humans associate with sadness. It's a sophisticated mimic, not a conscious being.
Key Takeaway: Today's AI is a master of imitation and pattern-matching within very specific boundaries. It's a powerful tool, but it doesn't possess the consciousness, creativity, or emotional depth that makes us human.
Is AI Dangerous or Something to Be Afraid Of?
Like any powerful technology, from the printing press to the internet, AI has real risks that we need to manage thoughtfully. The immediate worries aren't about sci-fi superintelligence taking over the world. The challenges we're facing right now are far more practical.
Here are a few of the big ones:
- Algorithmic Bias: If you train an AI on biased data from our imperfect world, the AI will learn and even amplify those biases, leading to unfair decisions in things like hiring or loan applications.
- Job Displacement: AI-powered automation is already changing the job market. While it will certainly make some jobs obsolete, it's also creating entirely new roles that didn't exist a decade ago.
- Data Privacy: AI systems are data-hungry. This creates a huge challenge around how our personal information is collected, used, and protected, especially as these systems become more integrated into our lives.
The solution isn't to fear the technology but to demand responsible development, ethical guidelines, and transparent governance. It’s on us to make sure AI is built and used for good.
How Can I Start Learning More About AI Myself?
It's never been easier to start learning about AI, and you definitely don't need a Ph.D. in computer science to get your bearings.
A great starting point is checking out free introductory courses on platforms like Coursera or edX, which have fantastic classes from top universities. Another simple habit is to follow a few well-respected AI researchers and tech publications online. The more you immerse yourself in the conversation, the more you'll find the core ideas start to click.
Ready to make sense of the technology shaping your world? At Simply Tech Today, we break down complex topics into clear, practical insights. Stay informed and confident in your tech knowledge by subscribing to our newsletter for the latest updates delivered right to your inbox. Learn more at https://www.simplytechtoday.com.

Member discussion