What is Edge Computing? How It Powers Your Smart Devices

Think of edge computing as a simple but powerful idea: instead of sending your data on a long journey to a faraway server, why not process it right where it's created? This simple shift brings data processing closer to you—right to the edge of the network—which cuts down on lag and makes your smart devices feel lightning-fast.
What Is Edge Computing, Really?
Let’s use an analogy. Imagine you're trying to stream a 4K movie, but the server holding the film is on the other side of the world. You’d probably spend more time staring at a buffering wheel than watching the movie. But what if a small server in your own neighborhood had a copy? The stream would be instant and flawless. That’s the essence of edge computing.
It's a model that moves computation away from a centralized cloud and brings it closer to the source of the data itself. This "at the source" processing is what makes so many modern technologies work seamlessly. It's why your phone's facial recognition can unlock instantly, even without an internet connection, or how a smart speaker can answer a command in the blink of an eye.
Why Does "Closer" Mean "Better"?
This local approach is absolutely essential for anything that requires split-second decisions. Edge computing is the backbone of the Internet of Things (IoT), where billions of connected devices—from sensors on a factory floor to smart traffic lights—are constantly churning out data. Sending every bit of that information to the cloud would be a bottleneck. To get a better sense of this interconnected world, check out our guide on what is the Internet of Things.
Instead of one massive, distant brain (the cloud), edge computing uses many small, local brains to think on the spot. This distributed intelligence makes technology faster, more reliable, and more private.
The growth here is hard to overstate. The global edge computing market is expected to balloon from USD 554.39 billion in 2025 to a staggering USD 6 trillion by 2035. This massive expansion is fueled by the need for instant data analysis everywhere—in our cars, our homes, and in industries where even a millisecond of delay can make a huge difference. You can dive deeper into this market forecast on Precedence Research.
How Edge Computing Actually Works
To really get what edge computing is all about, let's step away from the abstract definitions and look at how it functions in the real world. Think about a smart security camera you might see in an office. Traditionally, that camera would have to stream its video feed, 24/7, all the way to a server farm hundreds of miles away. That's a ton of data clogging up the internet pipes, and it’s slow.
Edge computing basically gives that camera its own brain. Instead of dumbly sending everything it sees to the cloud, a small but powerful computer—an edge device—is placed right there on-site. It might be a small box on the wall or even built directly into the camera itself.
Now, instead of shipping off hours of raw footage, the camera’s edge device analyzes the video in real-time. It acts as a smart filter, programmed to look for specific things, like a person trying to open a secure door after 9 PM.
The Local Decision-Making Process
This on-the-spot analysis is the heart and soul of edge computing. The device doesn’t just record data; it understands it and can act on it immediately.
Here’s how that plays out:
- Data Capture: The security camera is rolling, capturing its video stream.
- Local Analysis: Right there in the building, the edge device scans the footage, using its programming to spot movement or identify objects.
- Instant Action: If it sees a trigger event—that door opening after hours—it can take action instantly. Think sounding an alarm or sending a lock command. There’s no delay waiting for instructions from a distant server.
- Smart Reporting: Only after taking action does it send a tiny, relevant package of data to the cloud. This might be a 10-second video clip of the event and an alert, which gets logged for later review.
This whole process is far more efficient than the old-school, cloud-only method. The diagram below paints a clear picture of how different the data's journey is.
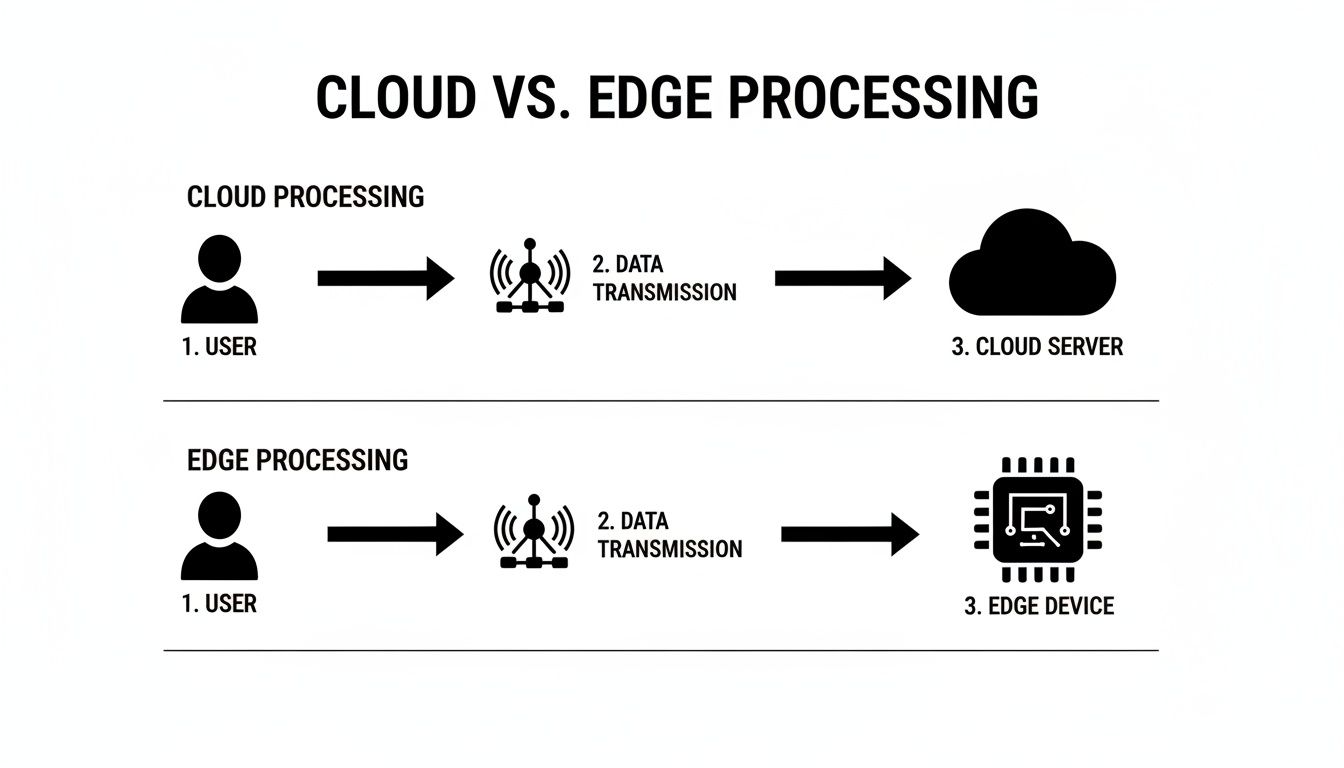
As you can see, the edge approach adds that critical local processing step, which drastically shortens the round-trip time for data and allows for those near-instant responses.
To help you quickly see the differences, here's a side-by-side comparison.
Edge Computing vs Cloud Computing At A Glance
| Feature | Edge Computing | Cloud Computing |
|---|---|---|
| Data Processing Location | Near the data source (e.g., on the device) | Centralized, remote data centers |
| Latency | Very low (milliseconds) | Higher (can be seconds) |
| Bandwidth Usage | Low; only essential data is sent | High; all raw data is transferred |
| Offline Capability | Yes, can function without an internet connection | No, requires a constant internet connection |
| Best For | Real-time decisions, IoT, immediate actions | Big data analytics, massive storage, backups |
This table shows they aren't competitors but partners with different jobs.
Cloud And Edge Working Together
This doesn’t mean the cloud is going anywhere. Far from it. The edge and the cloud actually make a fantastic team. The edge device is the frontline worker, handling the urgent, time-sensitive tasks on the ground. The cloud then acts as the central headquarters, taking care of the heavy-duty jobs like long-term storage, deep analysis of historical data, and training new AI models.
If you want to brush up on the cloud's role in this partnership, our guide on how cloud storage works is a great place to start.
Key Takeaway: Think of edge computing as a rapid-response unit. It processes data locally to make instant decisions and then sends only the important highlights up to the cloud. This saves a massive amount of bandwidth and nearly eliminates lag.
By filtering data right at the source, this model keeps internet traffic light and fast. It also gives privacy a major boost, since sensitive raw data—like all those hours of an empty hallway—never has to leave the building in the first place. This smart, hybrid system is what’s making so much of our modern, responsive technology possible.
The Real Benefits: Speed, Privacy, And Reliability
So, why does it even matter where your data gets processed? It turns out, it matters a lot. Edge computing isn't just some technical reshuffling happening behind the scenes; it’s about making the tech you use every day faster, more private, and more reliable when you really need it.These benefits all boil down to one simple, powerful idea: processing data locally is often just plain better.
Speed and Low Latency
The most obvious win is a massive boost in speed—or more accurately, low latency. Latency is just the technical term for the delay it takes for information to travel from your device to a server and back. In a fast-paced online game, a delay of just a few hundred milliseconds can be the difference between a win and a frustrating loss.
When your game console has to send every single button press to a cloud server hundreds of miles away, lag is practically guaranteed. Edge computing gets rid of that digital commute. By processing critical data right there on your local network, the experience feels instant and fluid, giving you the split-second responsiveness you need to compete.
Keeping Your Data Close To Home
Beyond just speed, edge computing offers a serious upgrade in privacy. Imagine you have a smart lock on your front door that you open with your fingerprint. In a typical cloud setup, your sensitive biometric data would have to travel across the internet to a server for verification, wait for a response, and then unlock the door. That journey, no matter how quick, opens up potential risks.
Edge computing flips that script entirely by handling the verification right on the device itself. Your fingerprint data never leaves your home. It’s processed locally, the lock opens, and your personal information stays exactly where it should—with you. This is a huge reason why people are starting to trust smart home technology.
Edge computing keeps your personal data close to home. By processing information at the source, it minimizes exposure and gives you greater control over who sees it.
Improving your digital security is always a smart move. For more ways to safeguard your information, you might be interested in our guide on how to protect your privacy online.
Uninterrupted And Reliable Operation
Finally, let's talk about reliability. Because edge devices can make decisions on their own, they don't need a constant, stable internet connection to the cloud to do their main job. If your Wi-Fi suddenly drops, a smart security system built on edge computing can still record events, trigger alarms, and keep your home secure.
That kind of self-sufficiency is a game-changer. It means your most important systems just keep working, even when the wider network is having a bad day. The need for this local processing is precisely why low latency is the top driver for edge adoption, cited by 41% of data professionals. Another 38.3% point to data privacy as their key motivator.
This groundswell of demand is helping the edge data center market balloon into what’s expected to be a $317 billion industry by 2026. You can explore more about these market trends and insights. By bringing together speed, privacy, and rock-solid reliability, edge computing delivers a fundamentally better and more resilient experience for all of us.
Edge Computing Examples You Already Use
The term "edge computing" might sound like something out of a sci-fi movie, cooked up for high-tech factories or smart cities of the future. The reality is, you're already surrounded by it. It’s the invisible workhorse that makes many of your favorite gadgets feel so responsive and intuitive, and you probably use it dozens of times a day without a second thought.
Once you know what you're looking for, you’ll start seeing edge computing everywhere. It’s not just some abstract concept; it’s a practical tool that powers the snappy, seamless experiences we now expect from our devices.

Your Smart Speaker's Instant Response
Ever wonder how your smart speaker perks up the instant you say "Hey Google" or "Alexa"? That's not magic—it's edge computing at its best. These devices are designed to constantly listen for a specific "wake word."
To pull this off without draining power or invading your privacy, a tiny, efficient processor inside the speaker handles this one simple task right there in your living room. It analyzes audio locally, which means it isn't sending a continuous stream of your private conversations to a server somewhere.
Only after the speaker detects its wake word does it "wake up" and begin sending your actual command to the cloud for the heavy lifting. This edge-first approach makes the initial response feel immediate while keeping your day-to-day chatter private.
This local processing is a key reason these devices have become so popular. If you're curious about how different brands implement this, our smart speaker comparison guide dives into their features and performance.
The Modern Car's Safety Systems
Modern cars are basically data centers on wheels, loaded with sensors, cameras, and computers. Many of the most critical safety features depend on edge computing to make split-second decisions that can save lives.
Think about these crucial technologies:
- Automatic Emergency Braking: When a car's sensors detect a potential collision, there's no time to send that data to the cloud and wait for an answer. An onboard computer has to process the information and slam on the brakes in milliseconds.
- Lane-Keeping Assist: Cameras constantly watch the lines on the road. A local processor analyzes your car's position in real-time and, if you start to drift, makes tiny, immediate steering adjustments to keep you centered.
- Adaptive Cruise Control: This system uses radar or cameras to maintain a safe following distance. All the calculations needed to speed up or slow down happen right inside the car, ensuring a smooth, safe reaction to the flow of traffic.
In every one of these scenarios, the vehicle itself is the edge network. It has to process vital sensor data locally because relying on a remote server would introduce a dangerous, unacceptable delay.
The Future in Plain Sight
Edge computing is also laying the groundwork for the next wave of technology that’s just now hitting the mainstream. For instance, smart retail stores use cameras and sensors to track inventory on shelves in real-time. This alerts staff when a product is running low without having to send massive video files to a central server for analysis.
Likewise, the next generation of augmented reality (AR) glasses will be completely dependent on edge processing. To overlay digital information onto your view of the real world without causing motion sickness, these devices need to process staggering amounts of visual data with virtually zero latency. That’s only possible by doing the hard work right on the device or a nearby hub, like your smartphone.
Weighing The Pros And Cons

Like any technology, edge computing isn't a one-size-fits-all solution. It offers some incredible upsides but also comes with a few trade-offs you need to be aware of. Looking at both sides of the coin helps us see where edge truly shines and where a traditional cloud setup might still be the smarter play.
The Key Advantages Of Edge Computing
The whole point of processing data locally is to gain some very real, tangible benefits that directly affect performance, security, and even your bottom line.
- Incredible Speed: By cutting out the round-trip journey to a distant data center, edge computing slashes latency. This is what allows for the near-instant responses needed for things like a self-driving car’s safety system or a seamless augmented reality experience.
- Stronger Data Privacy: When sensitive information like voice commands or security camera footage is processed right on your device, it doesn't have to travel across the public internet. This simple fact keeps your personal data far more secure and under your control.
- Reduced Bandwidth Costs: Instead of constantly streaming huge amounts of raw data, an edge device can analyze it locally and only send back important summaries or alerts. This smart filtering can save a fortune in internet bandwidth and lower operational costs.
- Greater Reliability: Edge devices are built to be self-sufficient. If your internet connection drops, your smart security camera can still record a break-in, and your factory’s quality control sensor can still function. The core tasks keep running.
The Current Challenges And Hurdles
For all its strengths, rolling out an edge computing strategy means confronting some practical and financial realities. These are the hurdles that any business will need to consider before jumping in.
The biggest one is the upfront hardware investment. It’s no surprise that hardware is projected to dominate the edge computing market, holding a 48% share by 2035, as companies buy the local servers and smart devices needed to make it all work. You can dig into more global edge computing market insights on Research Nester.
Managing and securing a sprawling network of potentially thousands of devices is a whole different ballgame than looking after a single, centralized cloud. Each device—or "edge node"—becomes another potential point of failure or a security risk that has to be monitored.
This complexity bleeds directly into security concerns. As the number of edge devices grows, so does the need to protect them. The edge security market is expected to skyrocket from USD 3.2 billion in 2021 to USD 12.6 billion by 2026.
Ultimately, choosing edge computing comes down to a balancing act. You have to weigh its powerful speed and privacy perks against the real-world costs and headaches of managing a widely distributed system. The logic behind these complex decisions shares some similarities with the processes explained in our guide on how artificial intelligence works.
Answering Your Key Questions About Edge Computing
As you start to wrap your head around edge computing, a few big questions usually come to mind. To really get the full picture, it helps to understand how it plays with the cloud, what it has to do with 5G, and where this is all going. Let's tackle those common questions.
I’ll break down each one in a way that’s clear and straightforward, building on what we've already covered and giving you a solid footing for what comes next in our connected world.
Does Edge Computing Replace The Cloud?
Not a chance. This is one of the biggest misconceptions out there—that edge computing is here to kill the cloud. The reality is that edge computing and the cloud are partners, not rivals. They’re designed to work together, with each one playing to its strengths to make the whole system better.
Think of it this way: the edge is your on-the-ground specialist, handling urgent tasks that need an immediate response. It’s the local expert making split-second decisions without having to phone headquarters. The cloud, then, is that powerful headquarters. It’s where the big-picture, long-term work gets done—heavy-duty data analysis, massive storage, and training those complex AI models.
For example, your smart doorbell (an edge device) processes motion and recognizes a face right there on your doorstep. But the cloud is where the full video history is securely stored for you to look back on later. This hybrid approach gives you the best of both worlds: the instant reaction time of the edge and the incredible horsepower of the cloud.
Is 5G Required For Edge Computing?
While it's not an absolute must, thinking of 5G and edge computing is like adding rocket fuel to a race car. Edge computing runs just fine on your standard Wi-Fi or 4G connection, but 5G is what truly unlocks its full potential. It creates an incredibly fast and stable connection between your devices and the local edge servers.
The two things 5G is famous for—ultra-low latency and massive bandwidth—are a perfect match for what edge computing is trying to achieve. It's this powerful duo that will make the most demanding, next-generation applications a reality.
Just imagine:
- Connected Vehicles: For self-driving cars to avoid collisions, they need to talk to each other and to smart traffic lights in real-time. That near-zero lag from 5G is non-negotiable for safety.
- Immersive Augmented Reality (AR): For AR glasses to feel real, they have to process what you're seeing instantly. 5G gives them the high-speed pipeline they need to offload some of that work to a nearby edge server without you ever noticing a delay.
So, while you don't need 5G for every single edge application, it's the key that will unlock the most exciting and world-changing uses in the years ahead.
How Does Edge Computing Improve My Privacy?
Edge computing can give your privacy a serious boost by changing a fundamental rule about how your data is handled. The core idea is simple but powerful: keep your data local whenever you can. In a lot of traditional cloud systems, your personal information has to take a long trip across the open internet to get processed.
Think about the voice commands you give your smart speaker or the video from an indoor security camera. In a cloud-first setup, that raw data travels to a corporate server somewhere far away. Every single step on that journey is a potential weak spot.
Edge computing flips the script by processing that data right on your device or on a local hub inside your home. This means the most sensitive information—like the inside of your living room—might never even leave your personal network, which dramatically cuts down its exposure to hackers or misuse.
This "local-first" approach gives you far more control over your own information. It's a big reason why edge computing is becoming the new standard for privacy-conscious smart home tech.
What Is The Future Of Edge Computing?
The future is incredibly exciting, and it all revolves around a concept called Edge AI. This is where artificial intelligence isn't just running in a massive data center, but right on the devices in your hand or in your home. Fusing AI with edge computing will make our gadgets smarter, faster, and far more independent.
Picture a smartphone that can do complex language translation on the fly, even when you have zero cell service. Or a health tracker on your wrist that doesn't just log your heart rate but actively analyzes it in real-time to spot an issue and alert you instantly.
This shift means our technology will feel more responsive and personal. Instead of our devices constantly needing to "phone home" to the cloud to think, they'll have the intelligence to understand and act right where they are, right when it matters.
At Simply Tech Today, our goal is to make sense of these important shifts in technology. To stay updated with clear, easy-to-understand explanations of the tech that shapes your world, explore more of our guides at https://www.simplytechtoday.com.

Member discussion