What Is the Internet of Things Explained

So, what exactly is the Internet of Things? Stripped of all the jargon, it’s simply a network of everyday objects that have been fitted with sensors and software to connect them to the internet. This connection gives them a digital voice, allowing them to gather and share information with us—and with each other.
Your Introduction to the Internet of Things
Let's think about a simple example. Imagine your morning alarm rings, and that action automatically signals your coffee maker to start brewing a fresh pot. That simple communication between two otherwise ordinary devices is the whole idea behind the Internet of Things. It isn't about some far-off future; it's about making the things we use every day smarter and more helpful.
This technology essentially builds a bridge between our physical world and the digital one. Items that were once completely offline—think thermostats, cars, or even factory machinery—can now sense what’s happening around them, report back, and even act on new instructions. It's this flow of information that unlocks incredible new ways to automate tasks and work more efficiently.
And this network is growing at an incredible pace. Just back in 2016, there were a little over 6 billion connected IoT devices around the world. Fast forward, and forecasts now predict that number could explode to 125 billion by 2030. That’s a massive shift set to reshape our homes, cities, and entire industries. You can get a deeper look at this growth from research by Fortune Business Insights.
The Four Core Components of IoT
To really get a handle on how this all works, it’s best to break it down into four essential parts. Think of these as the fundamental building blocks that turn any regular object into a "smart" one.
The Internet of Things is the concept of connecting any device (so long as it has an on/off switch) to the Internet and to other connected devices. The IoT is a giant network of connected things and people – all of which collect and share data about the way they are used and about the environment around them.
The table below gives a quick snapshot of these four components. We'll dive into each one right after, but this gives you a great starting point.
The Four Core Components of IoT
| Component | Simple Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Sensors/Devices | These are the "senses" of the object, collecting data from the physical world (like temperature, motion, or location). |
| 2. Connectivity | This is the "nervous system" that sends all that data to the cloud, using things like Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular networks. |
| 3. Data Processing | This is the "brain" of the operation. Software in the cloud analyzes the data to make sense of it and find useful patterns. |
| 4. User Interface | This is how you see and control everything, usually through an app on your phone that shows you the information and lets you take action. |
Together, these four pieces create a seamless loop: a device senses something, sends that information over a network, the data gets processed into something useful, and you get the final result on your screen. It’s a simple concept that powers an incredible amount of modern technology.
How an IoT System Actually Works
To really get what the Internet of Things is all about, it helps to look under the hood at how all the pieces fit together. At its heart, an IoT system is a simple, continuous loop with four key stages. Think of it as a conversation happening in the background—turning something happening in the real world into information you can actually use.
The whole process is about gathering data, sending it off to be analyzed, and then presenting it in a way that makes sense and lets you take action. Let's walk through that journey, step by step.
This diagram shows you the basic flow: a device grabs some data, shoots it over a network to a central hub in the cloud, and then sends back useful insights.
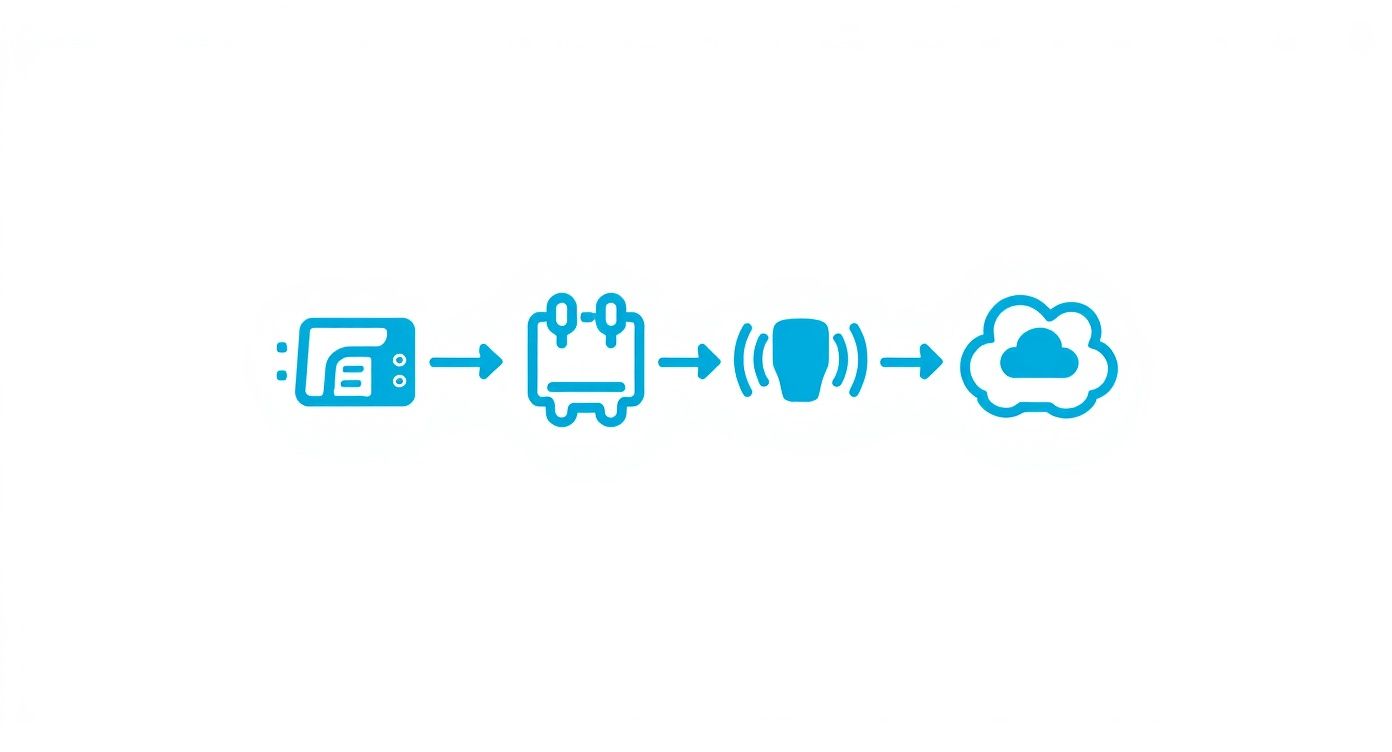
You can see how a regular physical object becomes part of a bigger, smarter network by passing information through these distinct stages.
Stage 1: Devices and Sensors
Everything in an IoT system starts with devices and their sensors. These are the "senses" of the operation, collecting raw data from the physical environment. Just like our eyes and ears gather information about what's around us, these little electronic components do the same for everyday objects.
For example, the sensor in a smart thermostat is constantly measuring the room's temperature. A motion detector in a security camera picks up movement. A GPS unit in a delivery truck logs its exact location. Each sensor's job is to translate a physical state—like heat, motion, or location—into a small piece of digital data.
Stage 2: Connectivity and the Network
Once a sensor has some data, it can't just sit there. It needs a way to phone home, and that’s where connectivity comes in. This is the nervous system of the IoT, creating pathways for that data to travel from the device to the cloud.
This communication happens over all sorts of networks, and the right one depends on the job:
- Wi-Fi: A great choice for smart home gadgets that stay in one place and need a steady, high-speed connection.
- Bluetooth: Perfect for short-range chats, like when your fitness tracker syncs up with your phone.
- Cellular (4G/5G): Absolutely essential for devices that are on the move, like connected cars or sensors spread out across a massive farm.
This stage is all about making sure the raw data gets from Point A (the sensor) to Point B (the brain) reliably.
Stage 3: Data Processing in the Cloud
After traveling across the network, the data lands in the cloud for processing. This is where the real "thinking" happens. Here, powerful software crunches the incoming streams of information, looking for patterns, flagging anomalies, and making decisions.
This isn't just about storing numbers; it's about finding meaning. For instance, the system might analyze temperature readings from a factory machine, notice it's running a little too hot, and automatically fire off an alert to the maintenance team. Much of this analytical muscle comes from advanced algorithms. If you want to dive deeper into that, our guide on machine learning for beginners is a great place to start.
An IoT system doesn’t just collect data; it transforms it into actionable insights. The processing stage is what turns a simple temperature reading into a predictive maintenance alert that can save a company thousands of dollars.
Stage 4: The User Interface and Action
The final stop on the journey is the user interface. This is how you interact with the system and see the results of all that data processing. It's usually an app on your phone or a dashboard on a website that presents the information in a clean, useful way.
This is where you get to see what’s going on and take action. You might get a notification that your smart doorbell spotted a package being delivered. You could look at a graph of your home's energy use over the last month. Or you could use an app to unlock your front door for a friend while you're still at work. This final step closes the loop, turning raw sensor data into something genuinely helpful.
Seeing IoT in Your Daily Life
You might think the Internet of Things is some far-off concept for tech gurus, but the truth is, it's already here. It’s working quietly in the background of your daily routine, making life a little easier and more efficient. From your morning coffee to the way traffic flows in your city, IoT is all around us. You're probably using it without even giving it a second thought.
These connected devices are everywhere, constantly gathering bits of information and making tiny adjustments that, together, make a big difference. They're in our homes, on our wrists, and built into the cities we navigate every day. Let’s look at some real-world examples that show just how connected our world has become.

IoT in Your Home
Your home is likely ground zero for your personal IoT experience. These gadgets, designed for everyday consumers, are all about automating chores, boosting comfort, and adding a layer of security. They just hop on your Wi-Fi, talk to each other, and use cloud services to create a smoother living experience.
Here are a few you've almost certainly seen:
- Smart Thermostats: Think of a Nest Thermostat. It learns your schedule and temperature habits, automatically dialing down the heat when you're out to save energy and warming things up just before you get home. It’s comfort and savings, all in one.
- Fitness Trackers: That Fitbit or Apple Watch on your wrist is a classic IoT device. It’s constantly tracking your steps, heart rate, and sleep quality, then sending all that data to an app on your phone. Suddenly, you have a clear, data-driven picture of your health.
- Smart Security Systems: Connected doorbells and cameras let you check on your front door from literally anywhere. You get alerts when someone approaches, can see recorded video, and even talk to a delivery person right from your smartphone.
These devices take everyday objects—a thermostat, a watch, a doorbell—and make them intelligent. They all work by sending the data they collect up to the cloud for processing. If you're curious about that part of the process, our guide on how cloud storage works breaks it down.
IoT in the Wider World
Beyond our front doors, IoT is making a massive difference in how industries and entire cities operate. This is often called the Industrial IoT (IIoT), and it’s all about using sensors and data to make large-scale systems run better. You may not see it directly, but you definitely feel its impact.
The growth here is staggering. By 2025, the number of IoT devices worldwide is expected to hit 21.1 billion. And looking further out, the industrial IoT market is projected to reach an incredible $2,146.07 billion by 2034. You can dig into more of the data in this eSparkInfo research.
This industrial-scale IoT is changing the game for how things get made and managed.
- Smart Factories: In manufacturing, sensors are attached to machines to monitor their health in real-time. This is called predictive maintenance. It allows factories to spot potential equipment failures before they happen, which prevents expensive shutdowns and keeps workers safer.
- Smart Cities: Local governments are using IoT to improve services for everyone. Connected traffic lights can analyze traffic patterns and adjust their timing to ease congestion. Smart trash cans can notify sanitation crews when they’re full, creating more efficient pickup routes that save time and fuel.
- Connected Agriculture: Farmers can now place sensors in their fields to monitor everything from soil moisture to crop health. This data helps them use just the right amount of water and fertilizer, which means bigger crop yields and less waste.
From the convenience of a smart kitchen to the efficiency of a high-tech factory, the Internet of Things is actively reshaping our world, one connected device at a time. To see the contrast clearly, here’s a quick comparison.
Consumer vs. Industrial IoT at a Glance
This table breaks down how IoT shows up in our personal lives versus how it's used in large-scale industries. While both use the same core technology, their goals and the scale of their impact are quite different.
| Category | Consumer IoT Example (Smart Home) | Industrial IoT Example (Smart Factory) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Convenience, comfort, and personal security. | Efficiency, safety, and cost reduction in large-scale operations. |
| Key Devices | Smart thermostats, fitness trackers, smart speakers, video doorbells. | Machinery sensors, automated robotics, supply chain trackers. |
| Data Usage | Personalizes user experience (e.g., adjusts home temperature). | Optimizes entire processes (e.g., predicts machine failure). |
| Scale & Impact | Affects an individual or household. | Affects an entire production line, factory, or supply chain. |
| Risk Focus | Data privacy and personal security. | Operational downtime, worker safety, and large-scale cybersecurity threats. |
As you can see, whether it's making your home feel more welcoming or preventing a factory from shutting down, IoT is all about using data to create smarter, more responsive environments.
The Pros and Cons of a Connected World
A world full of connected devices brings some incredible advantages, but it also forces us to make some important trade-offs. The Internet of Things isn't just about cool gadgets; it's about fundamentally changing how we manage our lives and resources. To really embrace this technology, you have to understand both its incredible power and its potential weak spots.
On one hand, IoT delivers a level of efficiency and insight that was pure science fiction just a few decades ago. On the other, it opens up a whole new can of worms regarding our data and digital safety. To get the full picture, we need to look at both sides of the coin.
The Major Benefits of IoT
The single biggest advantage of a connected world is efficiency. IoT systems can automate tedious tasks, make the most of our resources, and give us the data we need to make smarter choices. This pays off in real, tangible ways at home and in the workplace.
Think about these key improvements:
- Convenience and Automation: At home, this means automating the little things. Your lights can shut off when you leave the room, or your thermostat can adjust itself based on the forecast. It all happens in the background, without you lifting a finger.
- Real Cost Savings: In a factory, sensors on equipment can predict a failure before it happens, preventing an expensive breakdown. For a whole community, smart grids can manage electricity flow better, cutting down on waste and lowering everyone's energy bills.
- Better Safety and Security: A health tracker on your wrist can spot an irregular heartbeat and alert you or a family member, which could literally be a lifesaver. In the same way, connected cars can warn drivers about slick roads ahead or automatically call for help after a crash.
The magic behind all these benefits is the ability to collect data in real time and, more importantly, act on it. Many of these systems use complex algorithms to sift through that information and make intelligent decisions. You can get a better sense of the brains behind the operation by understanding how artificial intelligence works.
The Critical Risks and Challenges
Of course, connecting billions of devices to the internet also creates some serious challenges, mostly revolving around privacy and security. Every single smart device, if not properly protected, is another potential doorway for a cyberattack.
The very data that makes IoT devices so useful is also what makes them a target. Protecting this information is one of the biggest challenges facing the growth of the Internet of Things.
When you boil it down, the two biggest worries are crystal clear:
- Data Privacy: Your smart speaker, thermostat, and even your coffee maker collect an incredible amount of personal data about your daily routines and habits. It raises huge questions: Who owns that information? How are they using it? The risk of your data being sold or exposed without you knowing is a very real concern.
- Cybersecurity Threats: A cheap, poorly secured smart camera can be the weakest link in your entire home network. A hacker could get in and watch you, unlock your smart lock, or, in a bigger scenario, take over an entire factory's control system. The fallout from a breach like that could be devastating.
Getting the most out of IoT means striking a careful balance between its amazing potential and these very real risks. As more of us bring this technology into our lives and businesses, the push for stronger security standards and clear, honest data policies will only get louder. Knowing what's at stake is the first step to making smart, safe choices in our connected world.
How to Start Your Smart Home Journey
You don't need to be a tech wizard or have a huge budget to bring the Internet of Things into your home. The trick is to start small. Pick one useful gadget that solves a real, everyday problem. This way, you can get a feel for the technology without getting buried in complicated setups or a dozen new apps on your phone.
The key is to choose a first device that gives you an immediate, tangible win. Maybe you're tired of fumbling for the light switch in the dark or dream of waking up to the smell of freshly brewed coffee. Those simple victories make a connected home feel practical and real, and they'll probably get you excited to see what else is possible.

Choosing Your First Smart Device
Walking into an electronics store (or browsing online) can feel overwhelming. There are so many options. But instead of getting dazzled by fancy features, focus on three practical things to make sure you have a great experience right from the start.
Solve a Simple Problem First: Smart plugs and smart light bulbs are perfect entry points. They're affordable, a breeze to set up, and you get that "aha!" moment instantly. Right away, you can turn a lamp on from your couch with your voice or an app.
Check for Compatibility: Make sure any new device plays nicely with what you already own. If you’re an Alexa household or use Google Assistant, look for products that specifically say they work with those systems. This lets you control everything from one place instead of juggling different apps.
Put Security First: Stick with well-known, reputable brands that are upfront about providing regular security updates. That super-cheap, no-name device might be tempting, but if it doesn't get patched for security holes, it could leave your whole home network at risk.
Thinking about these points will help you pick a gadget that actually fits into your daily life and delivers real value, not just more complexity.
A Simple Setup Walkthrough
Let's imagine you bought a smart plug—one of the most common starter devices. The process is almost always straightforward and takes just a few minutes to go from the box to fully working.
Download the App: Head to your phone's app store, search for the manufacturer's app, and download it. You’ll probably need to create a quick account.
Plug In and Power On: Plug the smart plug into a wall outlet, then plug your lamp or coffee maker into the smart plug. You should see a little light on the plug start blinking, which means it's ready to connect to your Wi-Fi.
Follow the App's Lead: Open the app and it will guide you through adding a new device. You'll just need to pick your Wi-Fi network from a list and type in the password. Once it's connected, you can name it something descriptive, like "Living Room Lamp."
The second your device gets online, it’s talking to the cloud. This is where all your settings and schedules are safely stored, which is why you can control that lamp even when you're not at home. It’s a perfect example of the Internet of Things in action.
And just like that, you're done! You can now set schedules, create timers, or tell your voice assistant to turn the lamp on. All the heavy lifting with data happens quietly in the background. If you're curious about how that works, our guide explaining how to use cloud storage dives deeper into the basics. This one small, simple automation is your first step into a much smarter, more convenient home.
Common Questions About the Internet of Things
As you start to wrap your head around the Internet of Things, a few questions always seem to come up. It's a big topic that bumps up against other tech like artificial intelligence, and it brings up practical questions about everyday things, like your Wi-Fi at home. Let's tackle some of the most common points of confusion head-on.
Getting these details straight helps you build a solid foundation for understanding what IoT is and, just as importantly, what it isn't.
Is IoT the Same as Artificial Intelligence?
This is probably the most frequent question, and the short answer is no. But they are an incredibly powerful duo. It helps to think of IoT and AI as two specialists working together on the same project.
- The Internet of Things (IoT) is the field agent, the data collector. Its whole job is to gather raw information from the real world using sensors—things like temperature, motion, or location. IoT is the "senses" of the operation.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) is the analyst back at headquarters. Its job is to take the mountain of data that IoT collects and actually make sense of it. It looks for patterns, draws conclusions, and makes smart decisions. AI is the "brain."
A great example is a smart security camera. The camera itself is an IoT device; it captures video footage (that's the data gathering). An AI program then looks at that video and figures out if it's seeing a person, a car, or just the neighbor's cat (that's the data analysis). The IoT device provides the raw input, and the AI provides the smarts to do something useful with it.
IoT gives dumb objects a digital voice. AI gives them the brain to understand what they're saying and decide what to do about it.
Do I Need a Special Internet Connection for IoT?
For the vast majority of us at home, the answer is a simple no. The standard Wi-Fi connection you're already using for your laptop and phone is more than enough to handle smart speakers, light bulbs, and thermostats. Individually, these devices don't gobble up much bandwidth.
The catch is that the number of devices can eventually add up. If you start connecting dozens of smart gadgets and notice your internet is getting sluggish, it might be a sign that your router is feeling the strain. In that case, you might look into upgrading to a more powerful router or a mesh Wi-Fi system, which is designed to handle lots of connections smoothly. The internet connection is the same; you just need to make sure your home network is strong enough to manage all the traffic.
What Do Companies Do with My Data?
This is a big one. The data collected by your smart devices is incredibly valuable to the companies behind them. They typically use this information in a few ways. First and foremost, they study usage patterns to figure out how to improve their products. If they see that nobody is using a certain feature, they might scrap it or redesign it.
Secondly, many companies pool together anonymized data to identify big-picture trends. For example, a smart thermostat company might analyze data from an entire city to see how people adjust their heating during a cold snap, which can help with understanding energy consumption on a massive scale.
The most important thing you can do is read the privacy policy before you buy. It’s usually a dry read, but that document is where the company has to tell you exactly what data they're collecting and what they plan to do with it. Being an informed consumer is your single best tool for keeping your information safe.
At Simply Tech Today, we believe technology should be easy to understand. Our goal is to provide clear, practical guides that cut through the jargon. Explore more of our guides to stay informed.

Member discussion