Unlocking the Basics: what is vpn and how it works

Think of a VPN, or Virtual Private Network, as your personal bodyguard for the internet. It's a service that stands between you and the open web, shielding your connection and protecting your privacy online.
A VPN creates an encrypted, private "tunnel" for all your internet traffic. It also hides your real IP address (your device's unique identifier), which effectively masks your digital footprint and makes what you do online almost impossible to trace back to you.
What Is a VPN and Why You Might Need One
Let's use an analogy. Without a VPN, browsing the web is like sending a postcard. Anyone who handles it along the way can read the message—your internet service provider (ISP), the Wi-Fi network owner, and even cybercriminals lurking on the same connection.
A VPN is like taking that same postcard, sealing it inside a steel lockbox, and sending it via a private, armored truck. Nobody can peek inside. Only you and the intended recipient have the key.
This kind of digital lockbox is no longer just for tech experts; it's becoming a daily necessity. Every time you hop online, especially on a network you don't control, you're putting your personal information at risk.
To bring this home, let's walk through a few common scenarios where a VPN is a game-changer.
Everyday Scenarios Where a VPN Helps
- Using Public Wi-Fi: You know that free Wi-Fi at the coffee shop, airport, or hotel? It's an open playground for snoopers. A VPN encrypts everything you do, making your data unreadable to anyone else on that network.
- Maintaining Online Privacy: Your ISP can see every single website you visit, video you stream, and file you download. A VPN scrambles this information, keeping your browsing habits private from prying eyes. This is a key part of learning how to protect your privacy online.
- Securing Remote Work: If you work from home or travel, a VPN creates a secure, encrypted link back to your company's network. This ensures that sensitive business data stays safe from interception while it's in transit.
It's no surprise that more people are turning to VPNs for peace of mind. The demand for this kind of security is skyrocketing, with VPN usage in the United States alone jumping by 53% in just one year.
To make it even clearer, here's a quick breakdown of what a VPN really does for you in practice.
VPN at a Glance: Your Quick Guide
This table breaks down the core functions of a VPN and shows how they translate into real-world benefits.
| Core Function | What It Does for You | Real-World Example |
|---|---|---|
| Encryption | Scrambles your internet traffic into unreadable code. | Prevents a hacker at a coffee shop from stealing your credit card details when you're shopping online. |
| IP Masking | Hides your real IP address and replaces it with one from the VPN server. | Stops websites and advertisers from tracking your physical location and building a profile on you. |
| Tunneling | Creates a secure, private pathway for your data through the public internet. | Ensures your ISP can't see that you're streaming a new movie or which specific websites you visit. |
Essentially, a VPN bundles these functions together to give you a powerful, all-in-one tool for online privacy and security.
How a VPN Creates Your Private Internet Tunnel
So, how does a VPN actually pull this off? Think of it as a three-layered security system for your internet connection. It combines a secret code, a secure pathway, and a clever disguise to shield your data from the moment it leaves your device. This process essentially turns the chaotic public internet into your own private highway.
Each step works together to keep your online activity private and anonymous. Let’s peel back the curtain and see what’s happening.
Step 1: Encryption — Scrambling Your Data
The very first thing your VPN does is apply encryption. Imagine you're sending a postcard, but instead of writing in plain English, you write it in a complex code that only your friend knows how to read. That's exactly what encryption does for your internet traffic. It scrambles everything into an unreadable mess using sophisticated algorithms.
This means if anyone tries to snoop on your connection—whether it’s a hacker at a coffee shop or even your own Internet Service Provider (ISP)—all they'll see is gibberish. Without the right "key" to decipher the code, your information is completely useless to them.
This diagram shows how your data flows from your device, through this protected tunnel, to the VPN server, and then out to the internet.
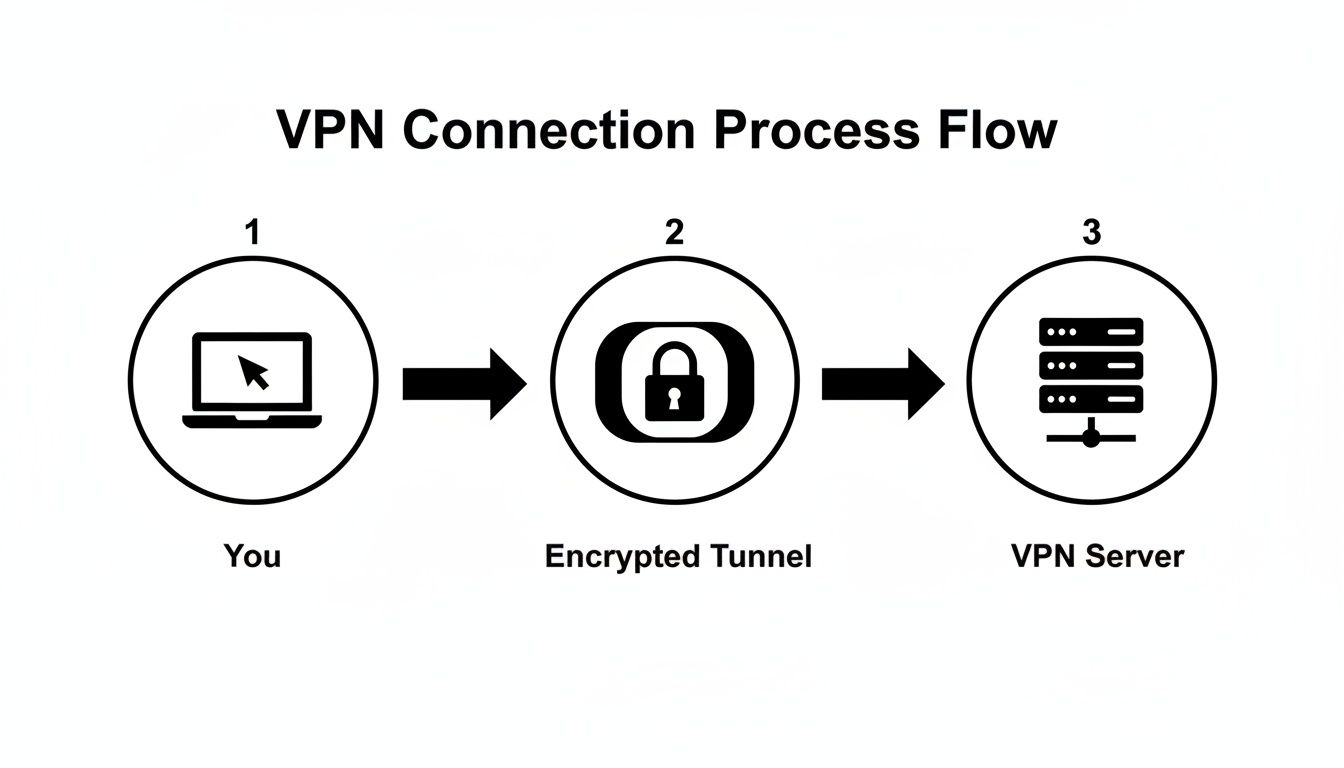
As you can see, the VPN acts as a secure intermediary. Your device never makes a direct, unprotected connection to the websites you visit.
Step 2: Tunneling — Building a Secure Pathway
Once your data is scrambled, the VPN creates a secure, private pathway for it to travel through. This is called tunneling. It’s like putting your data inside an armored truck that drives through its own private underground tunnel, completely hidden from all the traffic on the streets above.
This encrypted tunnel walls off your data from the rest of the public internet. Nobody can peek inside to see what sites you're visiting or what you're doing online. This is the core mechanism a VPN uses to deliver genuine privacy.
At its heart, a Virtual Private Network works by creating these encrypted "tunnels" for your data. When you connect, your traffic is scrambled and sent through this secure channel, making it unreadable to anyone trying to intercept it.
Step 3: IP Masking — Hiding Your Identity
The final piece of the puzzle happens when your encrypted data reaches the VPN server. This server now acts as your representative on the internet. It takes your request, sends it to the website you want to visit, and then returns the website's data to you. Crucially, it does all this using its IP address, not yours.
This is called IP masking. Think of it like sending a letter through a secure mail forwarding service in another city. The recipient only sees the address of the forwarding service, not your actual home address. This simple but powerful step hides your real-world location and stops websites, advertisers, and trackers from pinpointing who you are. The recent explosion in remote work, especially since the pandemic, is a major reason VPN use has skyrocketed. You can learn more about the growing VPN market in this detailed industry report.
Together, these three elements—encryption, tunneling, and IP masking—are the pillars of VPN security. They work in concert to give you a private, secure, and more anonymous way to use the internet, no matter where you are.
A Look Under the Hood: VPN Protocols
Not all VPNs are created equal. The engine that drives your private connection is called a VPN protocol, and it's what really defines how your VPN behaves. Think of protocols as different types of couriers for your data—some are built like armored trucks for maximum security, while others are like race cars, built for pure speed.
The protocol sets the ground rules for how your information is scrambled (encrypted) and sent on its journey. You don't need a degree in computer science to get it, but knowing the main players helps you understand why one VPN might feel zippier than another, or why one is better for your phone. Most good VPN apps actually let you switch between them, giving you a bit of control over the trade-offs.
Getting a handle on these protocols is a big step in truly understanding what a VPN is and how it keeps you safe.
The Most Common VPN Protocols You'll See
When you poke around in your VPN's settings, you'll probably run into a few specific names. Each one has its own personality and is cut out for different jobs, whether you're trying to stream a 4K movie without buffering or just want to make sure your connection doesn't die when you walk out of a coffee shop.
Here are the main protocols you'll find in almost any modern VPN:
- OpenVPN: This one's the veteran, the old reliable. For years, it has been the gold standard, offering a fantastic mix of rock-solid security and respectable speed. Because it’s open-source, countless security pros have picked it apart and confirmed it's trustworthy.
- IKEv2/IPSec: If you're on a phone or laptop, you'll love this protocol. IKEv2 (Internet Key Exchange version 2) is a champ when it comes to stability. It’s incredibly good at handling network changes, so if you switch from Wi-Fi to cellular data, it reconnects in a flash without you even noticing.
- WireGuard: The new kid on the block, and it's making a huge splash. WireGuard was designed from the ground up to be lean and mean. It uses far less code than older protocols, which translates to blistering speeds and better battery life on your devices, all while keeping security airtight.
A lot of tech experts, myself included, see WireGuard as the clear future. Its simplicity and speed are just that good. While OpenVPN is still a workhorse you can absolutely trust, WireGuard often delivers a noticeably faster experience, which is a huge win for gaming, streaming, or big downloads.
Which Protocol Should You Use?
So, which one is right for you? Honestly, for most people, the "Automatic" setting in the VPN app is the best choice. The software is smart enough to pick the optimal protocol for your connection.
But if you want to get hands-on, here's a quick cheat sheet:
| Protocol | Best For | Key Feature |
|---|---|---|
| OpenVPN | General use, especially on desktops where you want proven security. | The industry's most trusted and tested protocol. |
| IKEv2 | Anyone on a mobile device who moves around a lot. | Unmatched stability and fast reconnection. |
| WireGuard | Anything that needs speed: streaming, gaming, video calls. | The fastest and most efficient modern option. |
You might see older options like L2TP/IPsec or PPTP floating around, but they're outdated and have known security flaws. It's best to steer clear of them. Stick with OpenVPN, IKEv2, or WireGuard, and you'll be getting the security and performance you're paying for.
Practical Reasons to Use a VPN Every Day

It’s one thing to understand the mechanics of a VPN, but the real lightbulb moment happens when you realize just how useful it is in everyday life. A VPN isn't some niche tool for cybersecurity experts; it's a practical solution for common online situations.
Staying Safe on Public Wi-Fi
Think about the last time you hopped on the free Wi-Fi at a coffee shop, airport, or hotel. It’s convenient, but these public networks are notoriously insecure. They’re basically a digital playground for anyone trying to snoop on your data, leaving things like your passwords and banking details wide open.
This is where a VPN becomes your best friend. Before you connect, just switch on your VPN. It instantly wraps all your internet traffic in a layer of encryption, making it unreadable to anyone else on that network. Problem solved. That risky connection is now secure.
While a VPN is essential for safety on the go, it’s also smart to learn how to secure your home network for complete peace of mind.
Keeping Your Browsing Private
Even when you're on your trusted home Wi-Fi, you’re not as private as you might think. Your Internet Service Provider (ISP) can see every website you visit, every video you watch, and every online service you use. That browsing history can be logged and even sold to advertisers.
A VPN puts a stop to that. It encrypts everything before it leaves your device, so all your ISP sees is a jumble of code heading to a VPN server. They can tell you're using a VPN, but they have no idea what you're doing online. It’s a simple but powerful way to reclaim your digital privacy.
Key Takeaway: A VPN creates a secure, private connection by encrypting your data and masking your IP address. It's no wonder that over 1.5 billion people worldwide now use VPN apps for safer, more private browsing every day.
The sheer number of users shows that privacy is no longer a fringe concern. If you're curious about the numbers, you can dig into research on the growth of the VPN market and see the trend for yourself.
Accessing Your Content from Anywhere
Here’s another incredibly handy use for a VPN: getting around geo-restrictions when you travel. Ever been abroad and tried to watch your favorite show, only to be blocked because it's not available in that country? That’s geo-blocking in action.
A VPN neatly solves this. Just connect to a server back in your home country, and websites will think you’re browsing from your living room couch. You can log into your streaming accounts and access all the content you already pay for, no matter where you are in the world.
When to Use a VPN: Common Scenarios Compared
To make it even clearer, let's look at a few everyday situations. The table below breaks down common online activities, the risks involved without a VPN, and how a VPN provides a solution.
| Online Activity | Risk Without a VPN | How a VPN Helps |
|---|---|---|
| Using airport or cafe Wi-Fi | Unencrypted data can be easily intercepted by hackers on the same network. | Encrypts your connection, making your data unreadable to snoops. |
| Online banking or shopping | Financial details and passwords could be stolen on insecure networks. | Creates a secure tunnel directly to your bank or store's server. |
| Streaming from abroad | Your paid subscriptions (like Netflix or Hulu) might be blocked due to licensing. | Masks your IP address so you can access your home country's content library. |
| General web browsing at home | Your ISP can track and log every site you visit, then sell that data. | Hides your activity from your ISP, preventing them from monitoring you. |
As you can see, a VPN is more than just a security tool—it’s a key to a more open and private internet, giving you control over your digital life.
Understanding What a VPN Can and Cannot Do
A VPN is a fantastic tool for taking back control of your digital privacy, but it’s important to have realistic expectations. Think of it less as an impenetrable force field and more as a crucial piece of your security toolkit. Knowing what it does—and what it doesn't do—is the key to staying safe online.
Let's quickly touch on what a VPN does brilliantly. Its main job is to build a private, encrypted tunnel for your internet connection, making your online activity much harder for outsiders to see.
Its core strengths are:
- Hiding Your IP Address: It swaps your real IP address for one from the VPN server. This stops websites, advertisers, and snoopers from knowing your actual physical location.
- Encrypting Your Data: All the information traveling between your device and the VPN server is scrambled. This makes it completely unreadable to anyone trying to eavesdrop, including your own Internet Service Provider (ISP).
- Stopping ISP Tracking: Since your traffic is encrypted, your ISP can't see the specific websites you visit or what you do on them. Your browsing history stays private.
Where a VPN's Protection Ends
Now for the reality check. A VPN's protection has clear boundaries, and understanding them helps you avoid a false sense of security. It’s one powerful layer of protection, not the entire suit of armor.
First off, a VPN is not an antivirus program. If you download a shady file or click a malicious link in a phishing email, a VPN can't stop malware from infecting your device. For that, you still need reliable antivirus software running on your computer.
It also doesn't make you completely anonymous to the websites and services you willingly log into.
If you're signed into your Google, Facebook, or Amazon account, those companies still know it's you. A VPN can hide where you are, but it can't hide your actions on their platform once you've logged in and identified yourself.
Along the same lines, a VPN can’t block every tracking method out there. Websites use things like cookies and more advanced "browser fingerprinting" techniques to follow your activity across the web. These can still work even when your IP address is hidden.
Ultimately, a VPN is just one piece of a smart, layered security strategy. It works best when you pair it with other good digital habits, like using strong, unique passwords for every account and enabling multi-factor authentication.
For an extra layer of account security, it’s always a good idea to learn how to use two-factor authentication for your important online services. By understanding both its power and its limits, you can use a VPN to its full potential.
How to Choose and Use Your First VPN

Ready to dive into the world of VPNs? Getting started is surprisingly painless. With a little know-how, you can go from picking a provider to securing your connection in just a few minutes. The real trick is knowing what to look for and how to sidestep common traps, like those shady "free" services that might be selling your data on the side.
The most important thing is finding a provider you can trust—one that puts your privacy first. A good rule of thumb is to avoid any service with a vague privacy policy or a history of logging user data. You want a VPN that's completely open about how it operates and protects its users.
Core Features to Look For
When you're comparing different VPN services, a few features are absolutely essential. Think of these as the non-negotiables that form the foundation of a genuinely secure and private connection.
- A Strict No-Logs Policy: This is the big one. It's a promise from the VPN provider that they do not record, store, or share any of your online activity. If they don't have the data in the first place, they can't be forced to hand it over.
- Strong Encryption Standards: Make sure the service uses modern protocols like WireGuard or OpenVPN with AES-256 encryption. This isn't just jargon; it's the same security standard used by banks and governments to lock down sensitive information.
- Wide Server Selection: A large network of servers across many countries gives you more flexibility. You'll have more options for hiding your location and a better chance of finding a fast, stable connection no matter where you are.
Crucial Tip: Be extremely wary of free VPNs. They might seem like a great deal, but many of these services have to make money somehow—and it's often by collecting and selling your browsing data to advertisers and data brokers. That completely defeats the purpose of using a VPN.
Getting Started in Three Simple Steps
Once you've settled on a trustworthy provider, the setup process is a breeze. Modern VPN apps are designed to be incredibly user-friendly, often letting you connect with a single click.
- Sign Up and Download: Head to the provider's website, pick a subscription plan, and download the app for your device—whether it's a PC, Mac, or smartphone.
- Install and Log In: Just run the installer and sign in with the account you just created. The app takes care of all the complicated configuration behind the scenes.
- Connect to a Server: All you have to do is hit the "Connect" button. The app will usually find the fastest server for you automatically, or you can browse the list and pick a specific country yourself.
That's all there is to it. Your connection is now encrypted and your real IP address is hidden. If you ever run into problems, you may need to learn how to troubleshoot your internet connection, but for the most part, modern VPN apps just work.
Common VPN Questions Answered
Alright, let's tackle some of the most common questions that pop up when people first start looking into VPNs. These are the things most of us wonder about, so here are some straightforward answers to clear things up.
Will a VPN Make My Internet Slower?
It can, but it's usually not a big deal. Because a VPN adds extra steps—sending your traffic to a remote server and encrypting it—a slight speed drop is normal. Think of it like taking a scenic route instead of a direct highway; it adds a little extra travel time.
However, with top-tier VPNs, this slowdown is often barely noticeable for things like streaming, browsing, or gaming. In some weird cases, a VPN can actually speed things up if your Internet Service Provider (ISP) is purposely slowing down (or "throttling") certain types of traffic.
If you are noticing slow speeds, it's also worth checking your home setup. Learning how to improve your Wi-Fi signal strength can make a huge difference.
Am I Going to Get in Trouble for Using a VPN?
For most people, the answer is a clear no. In the vast majority of countries, using a VPN for privacy is 100% legal. Businesses and individuals rely on them every single day as a standard security tool.
The key thing to remember is that a VPN doesn't make illegal activities legal. And while it's rare, a few countries do have strict regulations or outright bans on VPNs, so it’s always smart to check the local laws if you're traveling abroad.
Can I Put a VPN on My Phone, Laptop, and TV?
You bet. Pretty much any quality VPN service provides apps for all the gadgets you own.
- Computers (Windows, macOS, Linux)
- Smartphones and tablets (iOS and Android)
- Streaming devices (Amazon Fire TV, Apple TV)
- Even your Wi-Fi router to cover every device in your home at once
Typically, one subscription lets you connect several devices at the same time. This means you can secure your laptop, your phone, and your smart TV all under a single account, whether you're at a coffee shop or on your couch.
At Simply Tech Today, our goal is to break down complex tech into simple, practical advice. Stick with us for more guides that help you stay safe and smart online. Find more insights at https://www.simplytechtoday.com.


Member discussion