Why Is My WiFi So Slow? Proven Fixes to Boost Your Internet Speed

Slow Wi-Fi can be incredibly frustrating, but the cause is often something simple. It could be anything from your router being tucked away in a cabinet, too many people streaming at once, or even just your internet provider having an off day.
The good news? You can usually fix these slowdowns in just a few minutes without calling for backup.
Your Quick Checklist for Slow WiFi Frustration
Before you start unplugging everything or spending an hour on hold with tech support, let's walk through the most common culprits. Think of this as a first-aid kit for your internet. We're not going to get into deep-level network diagnostics just yet. Instead, we’ll focus on the simple things that cause over 80% of all home Wi-Fi speed problems.
Following these steps in order will save you a ton of time and headaches. More often than not, the solution to "Why is my Wi-Fi so slow?" is surprisingly straightforward.
Start With the Easiest Fixes First
There's a reason "Have you tried turning it off and on again?" is the first question any IT pro asks. It works.
Before you do anything else, reboot your router. Unplug it from the power outlet, give it a full 60 seconds to completely power down, and then plug it back in. This one simple step can clear out all sorts of temporary glitches that build up over time.
Next, think about who—or what—is using your internet. Is your game console downloading a massive update in the background while someone else is streaming a 4K movie? Your internet bandwidth is a shared resource, and it’s not unlimited. Pausing large downloads or closing high-bandwidth apps on other devices can free up a lot of speed for what you're trying to do right now.
This flowchart gives you a great visual path for those first few troubleshooting steps.
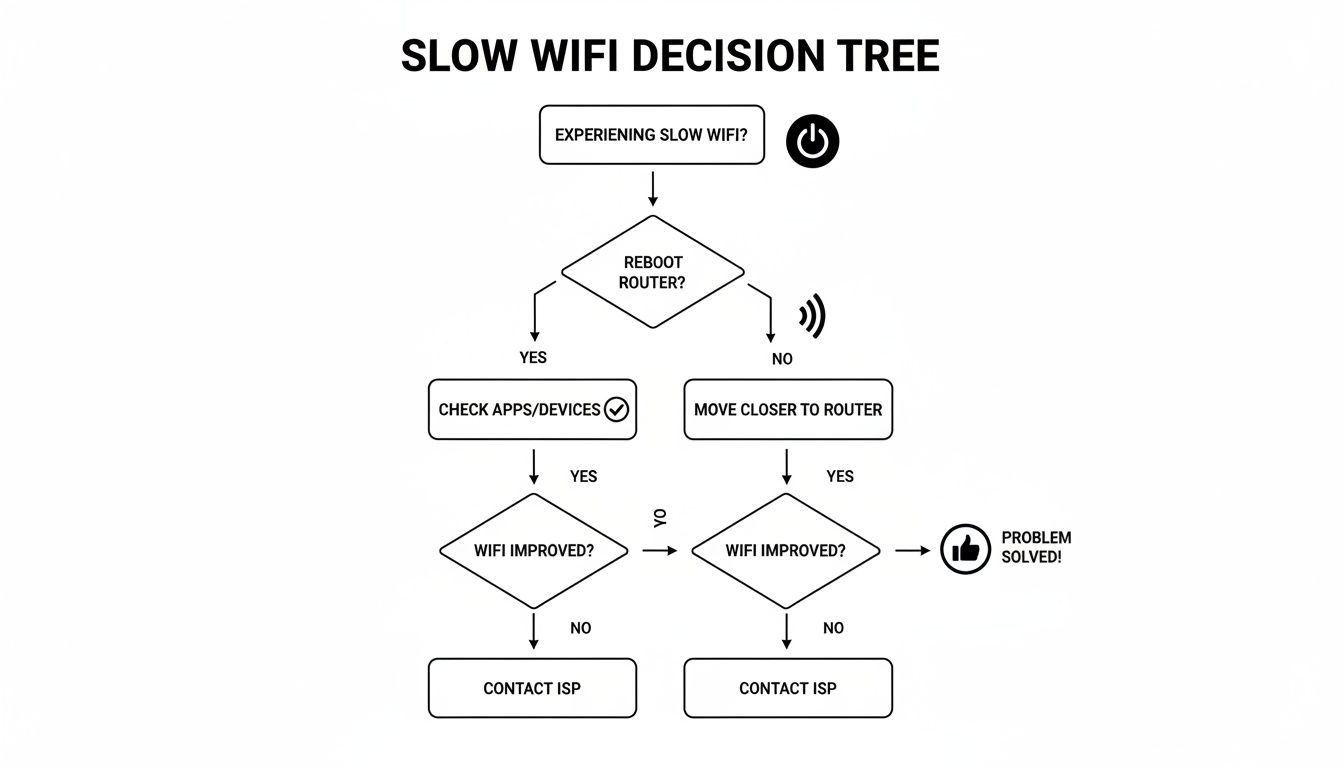
As you can see, a quick reboot is always the best place to start before digging into device-specific issues.
Common Problems and Quick Solutions
If the trusty reboot didn't do the trick, it's time to play detective. The table below can help you quickly match your specific problem to its most likely cause and give you a clear first step to take. This gets you from guessing to solving much faster.
This little cheat sheet helps you figure out if the problem is with your router, a specific device, or your internet plan itself.
Common Slow WiFi Causes and Quick Fixes
| Symptom | Likely Cause | Your First Action to Take |
|---|---|---|
| Wi-Fi is slow everywhere | Router Overload or ISP Issue | Reboot the router and modem |
| Wi-Fi is slow in certain rooms | Poor Router Placement / Weak Signal | Move closer to the router and test again |
| Wi-Fi is slow on only one device | Device-Specific Problem | Reboot the slow device |
| Wi-Fi slows down at the same time every day | Network Congestion (ISP or local) | Run a speed test during peak and off-peak hours |
| Buffering during video calls or streaming | Bandwidth Hogs | Pause downloads or streaming on other devices |
Remember, a slow internet connection can make your computer or phone feel sluggish, but sometimes the device itself is the bottleneck. If you suspect that’s the case, you might find our guide on how to speed up computer performance helpful.
Pro Tip: Don't try to troubleshoot from the other side of the house. For your first few tests, stand right next to your router. This immediately tells you if you're dealing with a weak signal or a different problem entirely.
Optimizing Your Router's Placement and Environment
If you’re constantly asking, "why is my Wi-Fi so slow?" the answer might be hiding in plain sight. Before you start fiddling with settings or getting on the phone with your internet provider, just take a good look at where your router is sitting. Its physical location is often the single biggest factor affecting signal strength and speed across your home.

Think of your Wi-Fi router like a speaker. You wouldn't stick it in a closet and expect the music to sound great in the next room. Wi-Fi signals radiate outwards in all directions, so hiding your router away in a cabinet, stuffing it behind the TV, or banishing it to a basement corner is a surefire way to kill your connection.
For the best coverage, your router needs to be in a central, open, and elevated location. Getting it up on a bookshelf or a small table in your main living space lets the signal travel much more freely to every corner of your house.
Battling Physical Barriers
Wi-Fi signals are just radio waves, and they have a tough time passing through certain materials. All sorts of things in your home can absorb, reflect, or just plain block those signals, creating frustrating dead zones where your connection crawls or drops completely.
Some of the most common signal killers are:
- Dense Materials: Concrete, brick, and even thick plaster walls are notorious for weakening Wi-Fi. The more walls the signal has to punch through, the weaker it gets on the other side.
- Metal Objects: Big metal appliances are like kryptonite for Wi-Fi. Your refrigerator, oven, and even metal filing cabinets can create a "signal shadow" behind them.
- Water: It sounds strange, but water is a surprisingly effective Wi-Fi blocker. A large fish tank or even the pipes in a radiant floor heating system can mess with your signal’s path.
The goal is to create the clearest possible line of sight between the router and the devices you use most. Every wall, door, or piece of furniture is another obstacle. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on how to improve WiFi signal strength.
Minimizing Electronic Interference
It’s not just physical objects that get in the way. Your home is full of other electronics that can broadcast on similar frequencies, creating a kind of "radio static" that drowns out your Wi-Fi signal. This is a very common, yet often overlooked, cause of a sluggish connection.
Your home is filled with devices competing for airwave space. The 2.4 GHz band, used by many routers, is particularly crowded because it's also used by microwaves, older cordless phones, Bluetooth speakers, and even baby monitors.
Try to keep your router at least three to five feet away from these common sources of interference. If you notice your internet cuts out every time you heat up leftovers, and your microwave is right next to your router, you’ve probably found the culprit. Sometimes, moving the router just a few feet is all it takes to give it the clear air it needs to communicate properly.
What About Your Internet Plan and ISP Throttling?
After you’ve sorted out your router’s place in the physical world, it’s time to look at the digital source of your connection: the internet service you’re paying for. Slow Wi-Fi isn't always about your gear. Sometimes, the problem lies with the plan you have or even how your Internet Service Provider (ISP) is managing its network.
You could have the best router money can buy, but it can’t invent speed you aren’t actually receiving from your provider. So, the first thing to check is whether you're getting the speeds you were promised in the first place.
Most internet plans are sold with an "up to" speed, like "up to 200 Mbps." Running a speed test is really the only way to find out what's actually being delivered to your modem. For a truly accurate reading, plug a computer directly into your router with an Ethernet cable. This simple test takes Wi-Fi completely out of the equation.
If that wired speed test shows numbers close to what you pay for, but your Wi-Fi still feels sluggish, the bottleneck is almost certainly somewhere in your home network. But if the wired speed is also surprisingly low, the issue is likely with your ISP.
Are You Getting What You Pay For?
Where you live dramatically affects the internet speeds available to you. While the worldwide median download speed for broadband has hit 104.4 Mbps, that number hides some massive differences from one place to another.
For instance, countries like Singapore can boast median speeds of 394.3 Mbps because they've invested heavily in fiber-optic infrastructure. Other regions lag far behind. This is why your neighbor with a different provider might have a completely different (and maybe much faster) online experience. You can dig into these global internet statistics to see just how much infrastructure impacts speed.
It’s also crucial to make sure your internet plan actually fits your household’s needs. A basic 50 Mbps plan might be perfectly fine for one person who just browses and checks email. But that same plan will buckle under the pressure of multiple people streaming 4K video, gaming online, and working from home all at once.
Key Takeaway: Think of your internet plan like a highway. If you have too many cars (devices) trying to cram onto a two-lane road (a slow plan), you’re going to get a traffic jam. Upgrading your plan is like adding more lanes—it lets more data flow smoothly at the same time.
The Mysteries of ISP Throttling and Network Congestion
Ever notice your internet slows down to a crawl around the same time every evening? You're probably experiencing network congestion. Think of it as a digital rush hour. When everyone in your neighborhood gets online at once to stream, game, and browse, it can overwhelm the local infrastructure. There just isn't enough total bandwidth to go around.
Another sneaky culprit could be ISP throttling. This is when your provider deliberately slows your connection down. They might do this if you’ve used a massive amount of data that month and hit an unwritten cap in your contract. Throttling is also a tool they use to manage their network during those peak hours, sometimes prioritizing certain types of traffic over others.
While there’s not much you can do to force your ISP to upgrade the whole neighborhood's network, you can sometimes sidestep targeted slowdowns. Using a Virtual Private Network (VPN) can help bypass certain types of throttling because it encrypts your traffic. This makes it much harder for your ISP to inspect what you're doing online and slow you down based on that activity. If that sounds interesting, you can learn more about what a VPN does and how it can help protect your privacy and connection.
Taming Bandwidth Hogs on Your Devices
Think of your Wi-Fi as a shared resource, like a water pipe to your house. If one person is running every faucet full blast, everyone else gets a trickle. The same thing happens on your network when a single device or application—a "bandwidth hog"—starts consuming way more than its fair share.
The culprit could be a 4K movie streaming on a tablet in another room, a massive game update downloading on a console, or a computer quietly syncing huge files to the cloud. You might not even realize it’s happening.

These silent speed killers often run in the background. Things like automatic software updates, constant cloud backups from services like Dropbox or Google Drive, and those hefty video game downloads are notorious for bringing a network to its knees, especially when they kick in at the worst possible time.
Identifying the Culprits on Your Network
So, how do you find out who’s hogging all the bandwidth? You’ll have to do a little detective work on your main devices.
On a Windows PC, pull up the Task Manager (Ctrl+Shift+Esc is a great shortcut) and click the "Network" column. This will instantly sort all active processes by how much data they’re using. For Mac users, the Activity Monitor does the same job—just head to the "Network" tab.
It’s just as easy on your phone:
- On Android: Go to Settings > Network & internet > Internet. Tap the little gear icon next to your Wi-Fi network and look for "App data usage." You’ll get a clear list of what’s been using your connection.
- On iOS: Head to Settings > Cellular. While this is technically for mobile data, it's a fantastic indicator of which apps are generally the most data-hungry.
Finding and managing these data hogs is a key part of keeping your network running smoothly and securely. For more tips on that front, our guide on how to secure your home network has some great, practical advice.
An Often-Overlooked Problem: Sometimes, it’s not a data-hungry app but a very old device. A phone or laptop with an ancient Wi-Fi card can force your brand-new router to slow down to its level, creating a bottleneck that impacts every other gadget you own.
Taking Control of Your Bandwidth
Once you've found the greedy app or device, you can start reining it in. A simple fix is to schedule big downloads and automatic updates for the middle of the night when everyone’s asleep.
For streaming, pop into the settings on services like Netflix or YouTube. Dropping the video quality from 4K to 1080p on a secondary screen, like a tablet, can free up a massive amount of bandwidth for everyone else without a noticeable difference in quality.
Dig into your router's settings, too. Many modern routers have a feature called Quality of Service (QoS). This lets you play traffic cop, telling your router to prioritize certain devices or activities. You can give your work laptop top priority during the day or make sure your gaming console always has the bandwidth it needs for a lag-free match. Spending a few minutes setting this up can completely change your daily internet experience.
Advanced Router Tweaks When Nothing Else Works
So, you’ve moved the router, kicked the bandwidth hogs offline, and your Wi-Fi still feels like it’s stuck in molasses. It’s time to pop the hood and get a little more hands-on.
Diving into your router’s settings might sound like a job for the IT department, but a couple of simple changes can make a world of difference. This is especially true if you live in a crowded area where your neighbor's Wi-Fi is interfering with yours. Think of it as switching your data from a bumpy backroad onto a freshly paved expressway.
Choose the Right Wi-Fi Band for Your Devices
Nearly every router sold today is dual-band, which just means it broadcasts two separate networks: one at 2.4 GHz and another at 5 GHz. They each have their own pros and cons, and strategically placing your devices on the right one is a game-changer.
- The 2.4 GHz Band: This is the old reliable. It reaches farther, but it's also slower and gets horribly congested. Everything from your microwave to your neighbor’s baby monitor can interfere with it. This band is best for low-priority gadgets that are far from the router, like smart plugs or a thermostat.
- The 5 GHz Band: This is the express lane. It’s much faster, much less crowded, and perfect for the things that need speed—your laptop, your smart TV, your game console. The only catch? Its range is shorter.
By manually assigning your most important devices to the 5 GHz network, you're essentially giving them a VIP pass to the fastest connection your router can offer.
Pro Tip: Many routers try to be clever by combining both bands under one Wi-Fi name (often called "band steering"). I find it’s better to log into your router’s settings and give them separate names, like "HomeNetwork_2.4" and "HomeNetwork_5". This puts you in full control.
Update Your Router's Firmware
Your router runs on its own internal software, called firmware. Just like your phone or computer, it needs updates. Manufacturers release these to patch security flaws, fix bugs, and, most importantly, improve performance. Most people set up their router and never touch it again, leaving a ton of speed and stability on the table.
Sometimes the real reason for slow speeds has nothing to do with your gear and everything to do with the pipes coming into your home. The biggest factor is often whether your neighborhood has fiber-optic internet. Just look at Singapore, which leads the world with 310 Mbps broadband speeds—they have 99% fiber coverage. Switching from an older cable or DSL connection to fiber can take you from 100 Mbps to 500+ Mbps literally overnight. You can see more details on which countries have the fastest internet connections.
To check for an update, you’ll need to log into your router's administration page (usually by typing an address like 192.168.1.1 into your browser). Look for a section called "Firmware Update" or "Router Update." Many modern routers can even handle this automatically, but it's always worth checking manually.
If you're still running into dead ends, it might be a bigger issue than just Wi-Fi. We have a broader guide on how to troubleshoot your internet connection that can help you diagnose problems beyond the router.
Still Stumped? Your Slow Wi-Fi Questions, Answered
Even after you've tried all the usual tricks, some Wi-Fi mysteries can be tough to crack. If you feel like you've hit a wall, let's walk through a few common scenarios that can help you figure out what's really going on.
Why Is My Wi-Fi Slow on Only One Device?
It’s a classic head-scratcher: your laptop is blazing fast, but your phone feels like it’s stuck in the mud. When this happens, the problem almost always lies with the device itself, not your internet connection.
Older gadgets often have outdated Wi-Fi hardware that simply can't handle today's faster speeds. Think of it like trying to play a modern video game on a ten-year-old computer—it just can't keep up.
Another common culprit is a background process. Your phone might be quietly syncing a massive photo library to the cloud, hogging all the bandwidth while your laptop sits idle. Dig into that device’s network settings to see if a specific app is being a data hog.
What's a Mesh Network, and Do I Actually Need One?
Imagine a mesh network as a team of routers working in perfect sync. Instead of relying on a single router to blanket your entire home, you place several smaller hubs, or "nodes," in different rooms. They all talk to each other, creating one big, seamless Wi-Fi network that eliminates dead spots.
You should seriously consider a mesh system if:
- Your home is large, has multiple floors, or has an unusual layout.
- You have thick walls made of brick, plaster, or concrete that block signals.
- You have frustrating "dead zones" where the Wi-Fi signal vanishes completely.
A traditional router is like a single speaker trying to fill a whole house with music—the sound will be faint in the far corners. A mesh system is like putting a speaker in every room, giving you perfect, consistent coverage everywhere. If you're tired of fighting dead zones, a mesh network is often the best long-term fix.
When Is It Time to Call My Internet Provider?
Before you brace yourself for a long phone call, you need to be sure the problem is on their end. The best way to do this is to bypass your Wi-Fi entirely.
Plug a computer directly into your router using an Ethernet cable and run a speed test. If the wired speed matches what you're paying for, the problem is with your Wi-Fi setup.
But if that direct, wired connection is still painfully slow, it’s time to pick up the phone. This test proves the issue is with the internet signal coming into your home. When you call, tell them the exact troubleshooting steps you’ve already taken—it'll help them skip the "did you try turning it off and on again?" script and get straight to the real problem.
At Simply Tech Today, we break down complex topics into simple, actionable advice. Find more clear, practical explanations to get the most out of your technology at https://www.simplytechtoday.com.

Member discussion